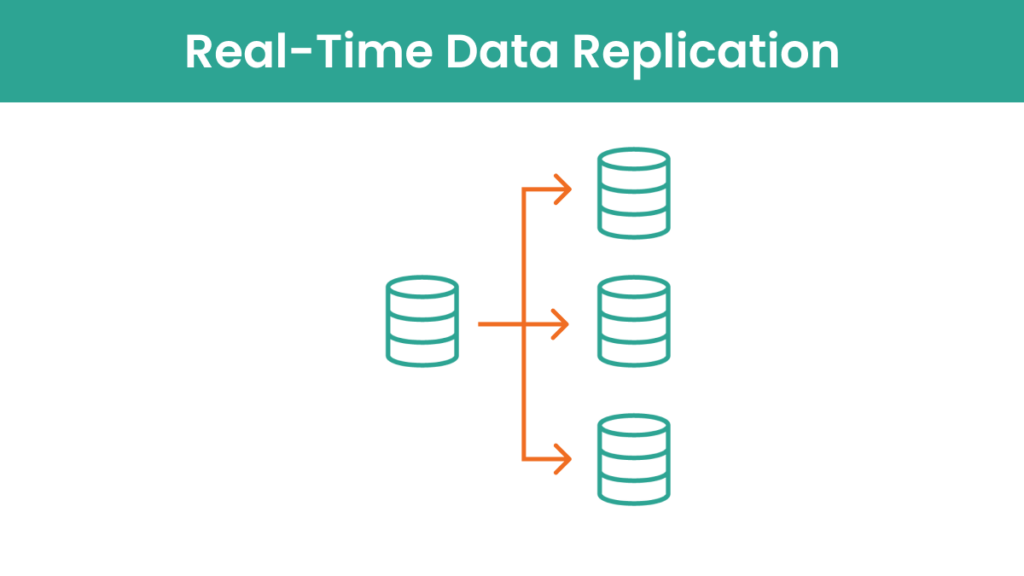
What is Real-Time Data Replication?
Real-time data replication is the near-instantaneous duplication and synchronization of data across multiple systems to ensure consistency, high availability, and support for disaster recovery in diverse environments, which is crucial for seamless operational continuity.
How Does Real-Time Data Replication Work?
Real-time data replication works by continuously monitoring changes in source data and immediately replicating these changes to one or more target systems. This process often utilizes change data capture (CDC) technology to detect changes in real-time without impacting system performance.
As changes are detected, they are transmitted almost instantly to the target database or system, ensuring that all systems maintain up-to-date and synchronized data. This mechanism is crucial for databases requiring high availability, consistent data across different locations, and robust disaster recovery protocols.
More Technical explanation:
For advanced users delving into the technical specifics of real-time data replication, the core mechanism is Change Data Capture (CDC). This technology efficiently identifies and logs changes at the data source (e.g., insertions in transaction logs, updates on customer records, and deletions from inventory databases) in real time. These changes are crucial for maintaining data integrity across transactional systems and data warehouses (e.g., Google Cloud, Snowflake, or AWS Redshift), such as updating real-time stock levels or syncing customer information across business units.
Without directly querying the database, CDC minimizes performance overhead and streams these changes incrementally to target systems. Employing a publisher-subscriber model, this approach supports a broad range of data integration and management use cases (e.g., integrating sales data into marketing platforms, and synchronizing order data across supply chain systems). It ensures consistent and up-to-date data across multi-platform and multi-database environments, facilitating complex IT landscapes in various industries.
What are the benefits of Real-time data replication?
Real-time data replication is pivotal in enhancing data management by allowing for continuous synchronization across systems. This process significantly reduces latency and improves data quality by ensuring that data remains consistent and updated across all platforms. Whether the systems are based on-premises or in the cloud, real-time replication helps maintain a reliable data environment.
The replication process leverages advanced technologies like APIs, connectors, and sophisticated replication software, including Kafka, Oracle, and PostgreSQL. These tools automate the data pipeline, integrating data ingestion, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes efficiently. This automation is crucial for managing large datasets and complex workloads, ensuring seamless data flow and accessibility.
Furthermore, real-time data replication supports robust data-driven decision-making, particularly critical during system outages. It offers scalable SaaS solutions that help manage extensive data volumes and optimize bandwidth usage. By maintaining compatibility with various schemas and focusing on data integrity, businesses can ensure high availability and adherence to stringent regulatory compliance requirements.
Real-time data replication provides several specialized benefits:
- Immediate Data Consistency: Guarantees real-time uniformity in data across distributed systems, crucial for applications requiring instant data accuracy.
- Enhanced Data Availability: Facilitates immediate data access from multiple geographic locations, significantly minimizing downtime and mitigating potential data loss during network or system disruptions.
- Robust Disaster Recovery: Ensures continuous data protection with instant failover capabilities, allowing businesses to quickly recover from system failures.
- Global Data Accessibility: Enables efficient, real-time data distribution across different geographical locations, optimizing performance and enhancing user experiences in global applications.
What is the difference between ETL and replication?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a batch-oriented process used for data integration. It involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it to fit operational needs or to cleanse it, and loading it into a data warehouse for analysis. This process typically happens at scheduled intervals, designed primarily for analytics and reporting purposes.
Replication, on the other hand, involves the continuous copying of data from a source database to one or more destinations. This process ensures that data remains synchronized across different systems or locations in real-time or near-real-time, enhancing data availability and supporting disaster recovery strategies. Replication is focused on maintaining operational consistency and data integrity across environments.
FAQs for Real-Time Data Replication
Q: What are the key technologies behind real-time data replication?
A: Real-time data replication primarily uses Change Data Capture (CDC) technology to track and replicate changes in real-time across various databases (e.g., SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL). This process ensures immediate data consistency and integrity across transactional systems and data warehouses.
Q: How does real-time data replication benefit disaster recovery plans?
A: Real-time replication plays a critical role in disaster recovery by ensuring data is continuously copied to secondary systems. This immediate replication minimizes data loss during outages and enables swift recovery, enhancing business continuity and data availability across multiple locations.
Q: What is the impact of real-time data replication on business decision-making?
A: By providing up-to-date and synchronized data across all systems, real-time data replication supports data-driven decision-making. This capability allows organizations to react quickly to market changes and operational demands, leveraging current data for strategic planning and operational adjustments.